
Welding is a skilled trade that combines precision, power, and creativity to join metal parts together. While the artistry of welding is impressive, the process itself involves several hazards that can pose significant risks to welders. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out, understanding welding safety and the essential personal protective equipment (PPE) is critical to working effectively and preventing injuries. In this in-depth article, we will explore every aspect of welding safety, with a primary focus on the PPE that every welder should have in their toolkit.
Why Welding Safety is Crucial
When you think about welding, you might picture sparks flying and metal glowing bright orange. While this imagery captures the excitement of the job, it also highlights the dangers welders face daily. The intense heat, bright light, molten metal, and toxic fumes involved in welding make it an inherently risky occupation. Without proper precautions, welders can suffer burns, eye damage, respiratory issues, and even long-term health problems.
Employers and workers alike have a responsibility to maintain a safe working environment by observing safety protocols and using proper PPE. Welding safety is more than just a set of rules—it’s a commitment to protecting your health and well-being so you can continue doing the work you love.
The Most Common Welding Hazards
Before diving into PPE, it’s important to understand the main hazards welders face. Identifying these hazards helps in selecting the right protective gear and adopting suitable safety measures. Some of the most common welding hazards include:
- Eye Injuries: The intense ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays produced during welding can cause “welder’s flash” or photokeratitis, a painful inflammation of the cornea.
- Burns: Hot sparks, molten metal, and the high temperature of welding tools can cause severe skin burns.
- Electric Shock: Welding equipment uses high voltage, which can lead to electric shock if safety practices are not followed.
- Fumes and Gases: Welding procedures produce hazardous fumes and gases that can cause respiratory problems or long-term health damage if inhaled.
- Noise: The loud noise generated by metal grinding and welding can damage hearing over time.
- Fire and Explosions: Sparks can ignite flammable materials nearby, leading to fire hazards.
Each of these hazards can be mitigated with appropriate welding safety techniques and PPE. Let’s explore the essential personal protective equipment required to keep welders safe.
Essential PPE for Welders: What You Need to Stay Safe

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) acts as the last line of defense against welding hazards. It is designed to shield welders from injuries by protecting their eyes, skin, lungs, and overall body. Below is a detailed breakdown of the essential PPE every welder should use.
1. Welding Helmet with Auto-Darkening Lens
Arguably the most critical piece of PPE for welders is the welding helmet. Its primary function is to protect the eyes and face from harmful rays, flying sparks, and hot debris. Modern welding helmets come with auto-darkening lenses that automatically adjust the shade depending on the intensity of the welding arc.
Here’s why welding helmets are indispensable:
- Eye Protection: UV and IR rays can cause severe damage to the eyes, leading to temporary blindness and potential permanent injury. The helmet filters out these harmful radiations.
- Face Shielding: Flying hot sparks and molten metal can cause facial burns and injuries. The helmet’s full-face coverage helps prevent these accidents.
- Auto-Darkening Technology: Allows welders to see clearly before welding begins and protects their eyes instantly when the arc is struck.
When selecting a welding helmet, consider these factors:
| Feature | Benefit | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Auto-Darkening Lens | Convenience and continuous protection | Cost and battery life |
| Viewing Area Size | Better visibility and comfort | Helmet weight and bulkiness |
| Adjustable Shade Levels | Flexibility for different welding types | Proper calibration required |
2. Welding Gloves
The intense heat and hazardous sparks produced during welding can cause serious hand injuries. Heavy-duty welding gloves are designed to provide heat resistance, flexibility, and durability. They also protect against cuts and abrasions from sharp metal edges.
Welding gloves are typically made from materials like:
- Leather (Cowhide, Goatskin, Deerskin): Durable and heat resistant.
- Kevlar Stitching: Adds strength and resistance to wear.
Here are some tips for choosing welding gloves:
- Pick gloves that provide a snug fit to maintain dexterity.
- Look for gloves with good gripping surfaces for handling tools safely.
- Make sure they cover wrists and lower forearms for additional protection.
3. Protective Clothing
Welding produces sparks and molten metal that can cause burns if your skin is exposed. Wearing protective clothing acts as a barrier between your skin and the hazards around you.
Common types of welding protective clothing include:
- Flame-Resistant (FR) Jackets: Made from treated cotton or leather which resists catching fire.
- Welding Aprons: Leather aprons protect the front body area from sparks and heat.
- Full-Length Pants: Durable pants made from fire-resistant materials protect your legs.
Guidelines for protective clothing:
- Avoid synthetic materials like polyester that can melt and stick to your skin.
- Wear long sleeves and long pants to minimize exposed skin.
- Ensure clothing fits comfortably without restricting movement.
4. Safety Glasses and Goggles
Even when wearing a welding helmet, safety glasses with side shields or goggles provide extra protection against flying debris and UV radiation. They are especially useful during grinding, chipping, and cutting tasks related to welding.
Key features to consider in safety glasses/goggles:
- Impact resistance (look for ANSI Z87.1 certification).
- UV protection.
- Comfortable and adjustable fit.
5. Respirators and Welding Fume Masks
Welding produces harmful fumes and gases that can affect respiratory health. Depending on the type of welding, protective respiratory gear may be necessary to prevent inhalation of toxic substances.
Types of respiratory protection include:
- Disposable Dust Masks: Provide minimal protection, mostly for grinding dust.
- Half-face Respirators with Filters: Offer better protection against fumes.
- Powered Air Purifying Respirators (PAPR): Provide filtered air and reduce fatigue during extended welding.
Using a respirator should be part of a comprehensive ventilation strategy including proper workspace ventilation and fume extraction systems.
6. Ear Protection
Welding can expose workers to loud noises, especially from grinding and cutting metals. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can cause irreversible hearing loss or tinnitus.
Types of ear protection include:
- Ear Plugs: Disposable or reusable, they reduce noise penetration.
- Ear Muffs: Provide a higher level of noise reduction and can be worn over ear plugs for maximum protection.
7. Safety Boots
Protecting your feet during welding is essential. Falling heavy metal pieces, sparks, and sharp debris on the floor can cause serious injuries.
Look for boots with these features:
- Steel Toe Caps: Protect toes from crushing injuries.
- Heat Resistant Soles: Prevent burns from hot materials on the floor.
- Slip Resistance: Prevents accidental falls in potentially slippery workshop environments.
How to Properly Use and Maintain Your Welding PPE

Having the right PPE is half the battle; knowing how to use it correctly and maintain it properly is equally important. Here are some best practices for using and caring for your welding safety gear.
Using Welding PPE Effectively
- Fit: Always ensure PPE fits correctly. Ill-fitting helmets, gloves, or masks can compromise safety and comfort.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect PPE for damage—cracks, worn parts, or broken straps—and replace as needed.
- Layering: Use multiple layers of protection as required. For example, safety glasses under a welding helmet for secondary eye protection.
- Practice Safe Habits: Always wear PPE before starting welding operations and throughout the process. Never remove gear mid-task.
Maintaining Your PPE
- Cleaning: Clean helmets, gloves, and clothing regularly to avoid buildup of dirt, sweat, and residues that could degrade materials or diminish protection.
- Storage: Store PPE in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight. Proper storage extends the lifespan of your gear.
- Battery Maintenance: For auto-darkening helmets, check and replace batteries regularly to ensure functionality during welding.
- Replace Worn Gear: Protect your health by replacing any PPE that shows signs of wear or malfunction.
Summary Table: Essential Welding PPE at a Glance
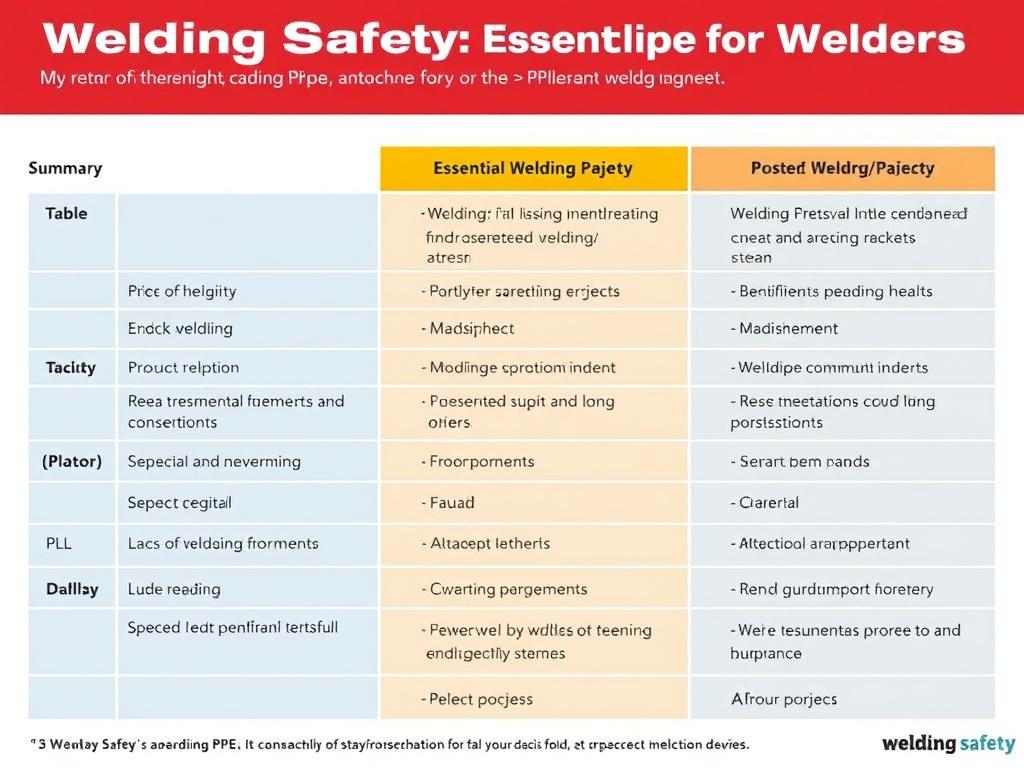
| Item | Purpose | Key Features | Maintenance Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding Helmet | Protects eyes and face from light, sparks, and heat | Auto-darkening lens, UV/IR protection | Clean lens regularly, check batteries, inspect shell |
| Welding Gloves | Protects hands from heat and sparks | Heat resistant leather, secure wrist coverage | Keep dry, clean, inspect for holes or tears |
| Protective Clothing | Shields skin from burns and sparks | Flame-resistant, long sleeves, sturdy material | Wash regularly, avoid synthetic fabrics, inspect seams |
| Safety Glasses/Goggles | Secondary eye protection during prep work | Impact resistant, UV protection | Clean lenses, replace scratched or cracked glasses |
| Respirators | Protects lungs from harmful fumes | Proper filter type, comfortable fit | Replace filters, clean mask, store properly |
| Ear Protection | Prevents hearing damage | Ear plugs or muffs, noise reduction ratings | Clean regularly, replace as needed |
| Safety Boots | Protects feet from impact and burns | Steel toe caps, heat resistant soles, slip resistant | Keep clean and dry, inspect soles and toes |
Additional Safety Tips for Welders
While PPE is essential, welding safety also involves following proper procedures and maintaining a safe work environment. Here are some extra tips to help you stay safe:
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Always weld in well-ventilated areas to reduce fume exposure.
- Keep Flammables Away: Remove combustible materials from your work area to prevent fires.
- Use Fire Extinguishers: Have appropriate fire-fighting equipment nearby and know how to use it.
- Training: Regularly participate in welding safety training to stay updated on best practices.
- Maintain Equipment: Inspect and maintain welding machines, cables, and tools to prevent electrical hazards.
- Ergonomics: Use appropriate welding positions and take breaks to avoid strain and fatigue.
Wrap-Up: Protect Yourself and Weld With Confidence
Welding is a rewarding profession that requires skill and dedication, but safety must always come first. By understanding the hazards and investing in the essential PPE outlined above, welders can dramatically reduce their risk of injury and health problems. Remember, every piece of your personal protective equipment has a specific purpose, contributing to your overall well-being in the workplace.
Take care of your PPE, use it correctly, and complement it with safe working practices. When you prioritize welding safety, you secure not only your current job but your long-term health. Stay safe, stay protected, and keep the sparks flying!
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on welding safety and essential PPE for welders. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional, embracing safety gear is the key to success in welding.
